Mycobonia brunneoleuca


Mycobonia brunneoleuca. Photo: Genivaldo Alves-Silva.
Mycobonia brunneoleuca is a saprotrophic fungi species that causes white rot in dead wood. There are 15 registers of the species so far, all of them being restricted to cloud forests and Araucaria forests in the Neotropical region. Five of these registers are from Costa Rica, three from Brazil, and one from each of these countries: Colombia, Honduras, Martinique, Panama, Paraguay, Porto Rico, and Venezuela. The species is divided into two subpopulations, one located in north tropical America and the other in southern South America. It is expected that the potential species distribution follows the pattern found in its known distribution, occurring throughout the Neotropical region in cloud forests and montane areas. The species populations are threatened by habitat loss which is caused mainly by deforestation and climate change. Still, cloud forests are susceptible to land conversion to exotic species cultivation such as Pinus and Eucalyptus. Other threatening factors are cattle grazing, hunting, fire, logging, mining, and roads construction. Therefore, the species is assessed as Vulnerable under IUCN criterion A3c.
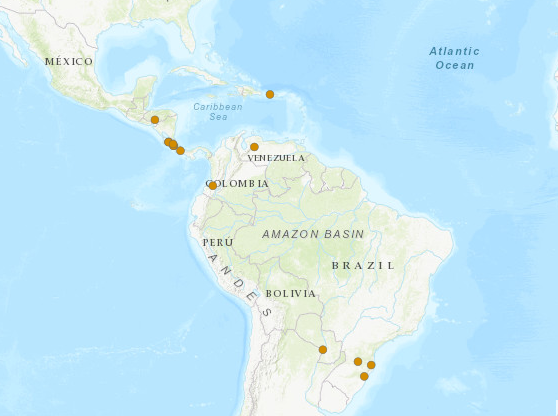
M. brunneoleuca distribution map. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/209595073/209596310#taxonomy.
References
Palacio, M., Westphalen, M., Gomez-Montoya, N., Benjumea, C., Alves-Silva, G., Martins da Cunha, K., Kossmann, T., Costa-Rezende, D.H., Trierveiler-Pereira, L., Baltazar, J.M., Vieira de Miranda, M. & Drechsler-Santos, E.R. 2022. Mycobonia brunneoleuca. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022: e.T209595073A209596310. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2022-1.RLTS.T209595073A209596310.en. Accessed on 03 August 2022.







